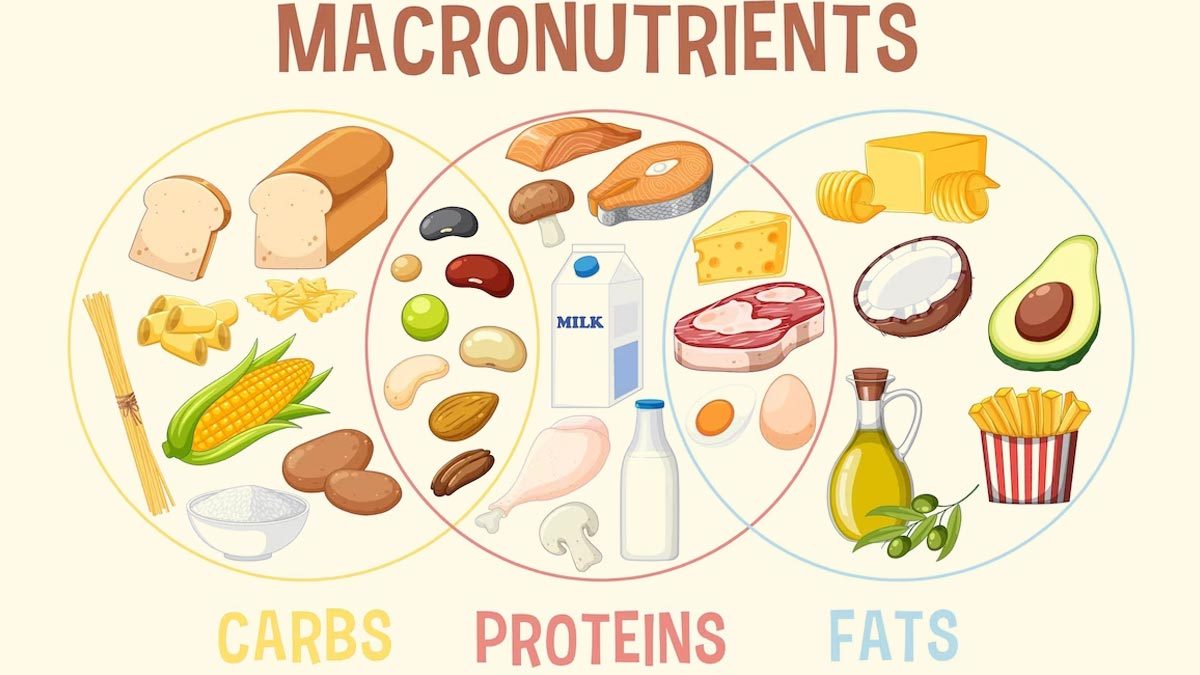
Macronutrients are the building blocks of our diet, providing the energy and essential nutrients our bodies need to function optimally. Understanding the roles of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is crucial for achieving a balanced and nutritious diet. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of macronutrients, exploring their functions, sources, and how to incorporate them into your diet for optimal health and well-being.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, providing fuel for daily activities and bodily functions. They are classified into two main categories: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, found in foods like fruits, refined sugars, and processed snacks, are quickly digested and absorbed, leading to rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and starchy foods, are digested more slowly, providing a steady and sustained release of energy.

Sources of carbohydrates:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, sweet potatoes
- Fruits: Berries, apples, bananas
- Dairy: Milk, yogurt (contain lactose, a naturally occurring sugar)
Incorporating carbohydrates into your diet:
- Choose whole, unprocessed sources of carbohydrates whenever possible.
- Aim to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your meals.
- Balance carbohydrate intake with protein and healthy fats to help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote satiety.

- Proteins: Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and regulating various physiological processes in the body. They are composed of amino acids, which are often referred to as the “building blocks of life.” While the body can synthesize some amino acids on its own, others must be obtained through dietary sources. Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids in sufficient amounts, while incomplete proteins lack one or more essential amino acids.
Sources of proteins:
- Animal sources: Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products
- Plant sources: Beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, edamame, quinoa, nuts, seeds
- Dairy alternatives: Soy milk, almond milk, oat milk
Incorporating proteins into your diet:
- Include a source of protein in each meal to support muscle repair and satiety.
- Experiment with a variety of plant-based protein sources to diversify your diet and meet your nutritional needs.
- Opt for lean cuts of meat and poultry and incorporate fatty fish like salmon and tuna for heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.

- Fats: Fats play a vital role in the body, serving as a concentrated source of energy, supporting cell growth and maintenance, and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). While fats have historically been demonized, it’s important to distinguish between healthy fats and unhealthy fats. Unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are considered heart-healthy and can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish. On the other hand, saturated fats and trans fats, found in processed foods, fried foods, and fatty cuts of meat, should be consumed in moderation as they can increase the risk of heart disease and other health conditions.
Sources of fats:
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds
- Olive oil
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, trout
- Plant-based oils: Coconut oil, avocado oil
Incorporating fats into your diet:
- Choose sources of unsaturated fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, to promote heart health and improve cholesterol levels.
- Limit intake of saturated fats and trans fats found in processed and fried foods.
- Aim to include a balance of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates in your meals to support overall health and well-being.
Macronutrients play essential roles in supporting overall health and well-being, providing the energy and essential nutrients our bodies need to thrive. By understanding the functions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats and incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet, you can optimize your nutrition and fuel your body for optimal performance. Whether you’re looking to improve energy levels, support muscle growth, or maintain a healthy weight, focusing on balanced macronutrient intake is key to achieving your health and wellness goals.
Keywords: Macronutrients, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, understanding macronutrients, sources of carbohydrates, sources of proteins, sources of fats, healthy fats, USA readers, balanced diet.
Yo may also Like: